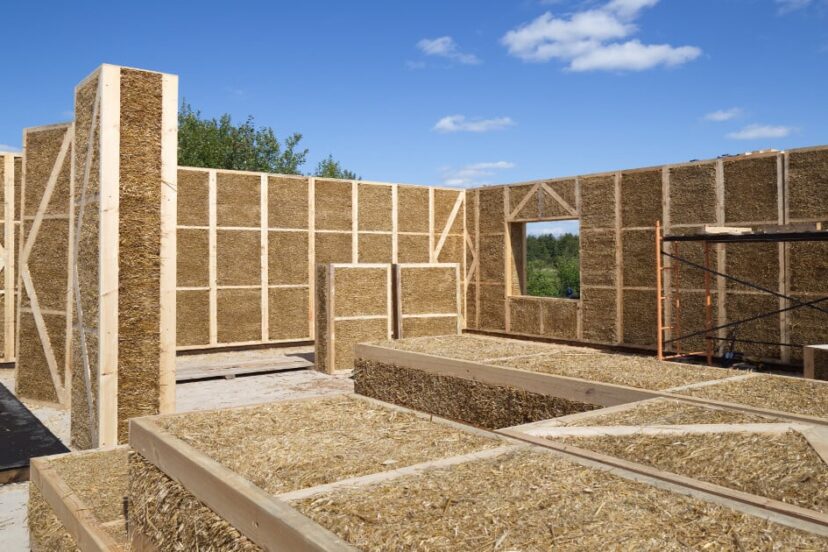
Eco-Friendly Building Materials in Tiny House Construction
Building a tiny house with minimal environmental impact is not only a trend but also a responsible choice for those who want to live sustainably. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about eco-friendly building materials for tiny houses. From choosing the right building products to reducing waste throughout the building process. Building an energy efficient home is just as important as specifying the right products to build with. There is a lot to unpack when it comes to the implementation of energy-efficient design principles and practices. I’ll cover Energy Efficiency in another post: Eco-Friendly Tiny House Energy Efficiency
Choosing Eco-Friendly Building Materials
Selecting the right materials is crucial when it comes to eco-friendly construction. By opting for sustainable materials, you can minimize your environmental footprint while still creating a comfortable and durable tiny home. From reclaimed wood to recycled steel, there are plenty of options to consider. If you are not sure what to specify, visit Green Building. A Canadian Resource for all things green. They have put together the “Green Building Guide to Sustainable Materials” which is a great reference. They also have a comprehensive Directory where you can find builders, trades and products. When planning your material list, it’s important to consider the location of products. Where you live makes a difference in what you specify due to a number of factors. The most obvious consideration being availability and shipping distance.
The geographical availability of materials plays a significant role in eco-friendly building material decisions. When selecting materials for a tiny home, it’s essential to consider not only their sustainability but also their sourcing and transportation footprint. Here’s how the geographical availability of certain materials can impact decision-making:
1. Local Sourcing: Opting for materials that are readily available locally can reduce transportation emissions and costs. For instance, using reclaimed wood from nearby sources or sourcing timber from sustainably managed forests in the region minimizes the carbon footprint associated with transportation
2. Recycled Materials: Materials such as recycled steel or reclaimed brick can often be sourced locally or regionally, depending on the presence of recycling facilities or salvage yards. Utilizing these materials not only diverts waste from landfills but also reduces the need for virgin resources and energy-intensive manufacturing processes.
3. Natural Materials: In regions with abundant natural resources like clay, straw, or earth, incorporating natural eco-friendly building materials such as adobe, cob, or straw bales can be both environmentally friendly and cost-effective. These materials are often locally sourced, renewable, and have low embodied energy, making them attractive options for sustainable construction.
4. Climate Considerations: Geographical location also influences material choices based on climate considerations. For example, in areas prone to extreme weather conditions, such as hurricanes or earthquakes, using resilient materials like bamboo or engineered wood and recycled steel can enhance the structural integrity of the tiny home while minimizing environmental impact.
5. Availability of Eco-friendly Building Material Alternatives: Some regions may have limited availability of certain sustainable materials, prompting homeowners to explore eco-friendly alternatives. For instance, if locally sourced reclaimed wood is scarce, they may opt for FSC-certified timber or alternative materials like bamboo, which has rapid regrowth rates and high sustainability credentials.
6. Energy Efficiency: Apart from the material itself, the geographical availability of energy-efficient building components like insulation or windows can also influence construction decisions. Choosing locally produced energy-efficient materials reduces emissions associated with transportation and enhances the overall sustainability of the tiny home.
In essence, by considering the geographical availability of materials, tiny homeowners can make informed decisions that minimize environmental impact, support local economies, and create durable, comfortable living spaces. Collaboration with local suppliers, builders, and sustainable design professionals can further optimize material choices for eco-friendly construction projects.
Reclaimed Wood: Embracing the Beauty of Salvaged Timber
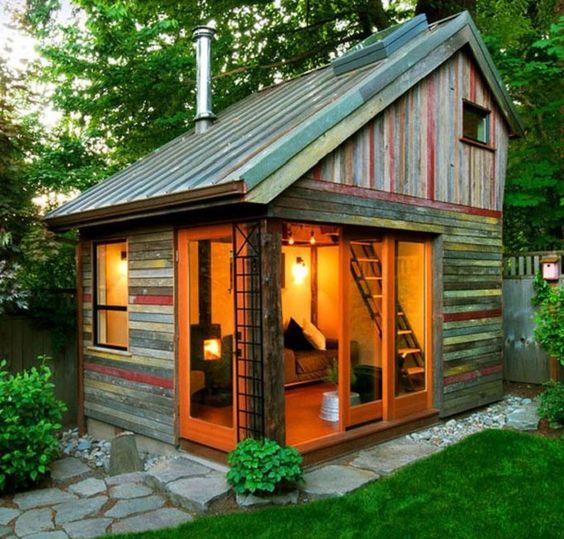

Reclaimed wood not only adds character to your tiny house but also reduces the demand for new timber, thus helping to preserve forests. Hear is how to source reclaimed wood and incorporate it into your construction projects.
First, sourcing reclaimed wood for a tiny house project requires a combination of research, networking, and creativity. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to find reclaimed wood:
1. Locate Reclamation Yards and Salvage Shops: Reclamation yards and salvage shops are treasure troves of reclaimed eco-friendly building materials, including wood. Research and visit local reclamation yards or salvage shops in your area to browse their inventory of reclaimed wood. These establishments often stock a variety of wood species salvaged from old barns, factories, warehouses, and other structures.
2. Connect with Demolition Contractors: Demolition contractors often salvage reusable materials from buildings slated for demolition, including lumber. Reach out to demolition contractors in your area and inquire about any upcoming demolition projects. They may be willing to sell or donate salvaged wood from these projects, providing you with a sustainable source of reclaimed lumber for your tiny house.
3. Explore Online Marketplaces: Online marketplaces such as Craigslist, Facebook Marketplace, and eBay can be valuable resources for finding reclaimed wood. Browse listings in your area or post a “wanted” ad specifying the type and quantity of reclaimed wood you’re looking for. Additionally, there are specialized online platforms dedicated to reclaimed building materials where you can find a wide selection of reclaimed wood from various sources.
4. Attend Salvage Auctions or Events: Salvage auctions or events hosted by reclamation yards, architectural salvage companies, or nonprofit organizations are excellent opportunities to find reclaimed wood at competitive prices. Attend these events to bid on or purchase reclaimed wood directly from sellers. You may also network with other attendees and learn about additional sources of reclaimed wood in your area.
5. Consider Deconstructing Old Structures: If you have access to an old structure scheduled for renovation or demolition, consider deconstructing it yourself to salvage usable materials, including wood. Obtain permission from the property owner and ensure compliance with local regulations before beginning any deconstruction activities. Be prepared for the labor-intensive nature of deconstruction and enlist the help of experienced professionals if needed.
6. Repurpose Existing Furniture or Pallets: In addition to traditional sources of reclaimed wood, consider repurposing existing furniture, pallets, or other wooden objects for your tiny house project. Old furniture pieces, shipping pallets, and discarded wooden crates can be disassembled and transformed into functional building materials for flooring, paneling, shelving, and more.
By exploring these avenues and thinking creatively, you can source high-quality reclaimed wood for your tiny house project while reducing waste and environmental impact. Additionally, consider the specific characteristics and requirements of reclaimed wood, such as species, dimensions, and condition, to ensure that it meets your needs and enhances the aesthetic appeal of your tiny home.
Recycled Steel: Strength and Sustainability in Tiny House Design
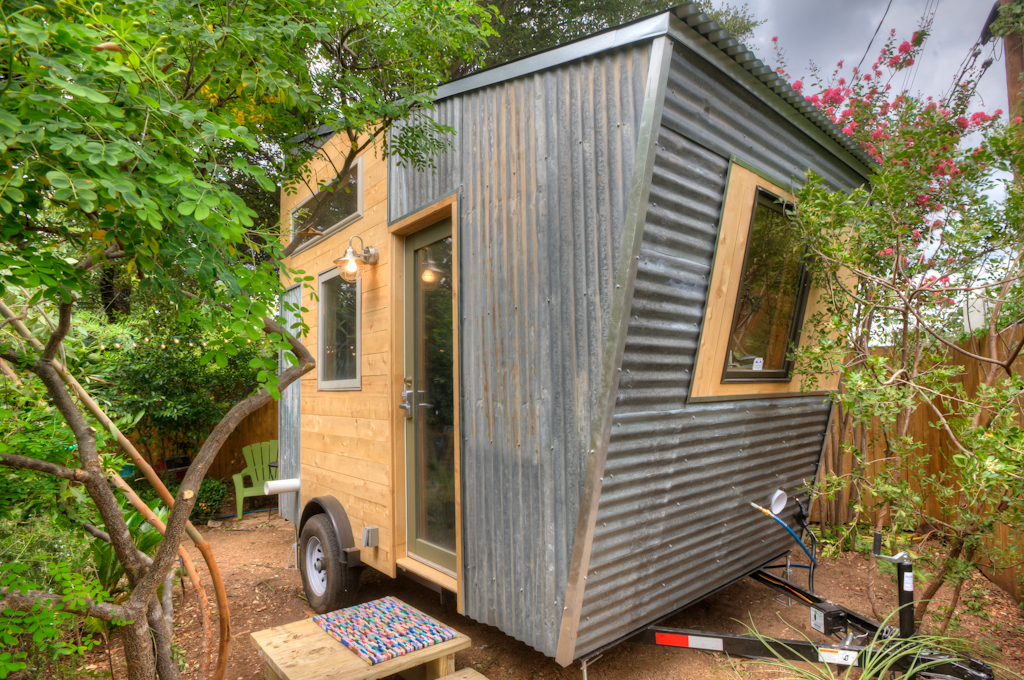

Steel is a versatile and durable building material that can be recycled indefinitely without losing its properties. Discover how recycled steel can be used to frame your tiny house and provide structural integrity while minimizing environmental impact. Recycled steel can be sourced from various sources, including industrial, commercial, and consumer sources. Here are some common sources for obtaining recycled steel:
- Scrap Yards and Recycling Centers
- Construction and Demolition Sites
- Automobile Recycling Facilities
- Industrial and Manufacturing Facilities
Repurposing recycled steel in tiny house building design offers numerous opportunities for creativity, sustainability, and structural innovation. Here are several ways to incorporate recycled steel into tiny house construction:
- Structural Framing
- Exterior Cladding and Siding
- Roofing Materials
- Interior Finishes and Detailing
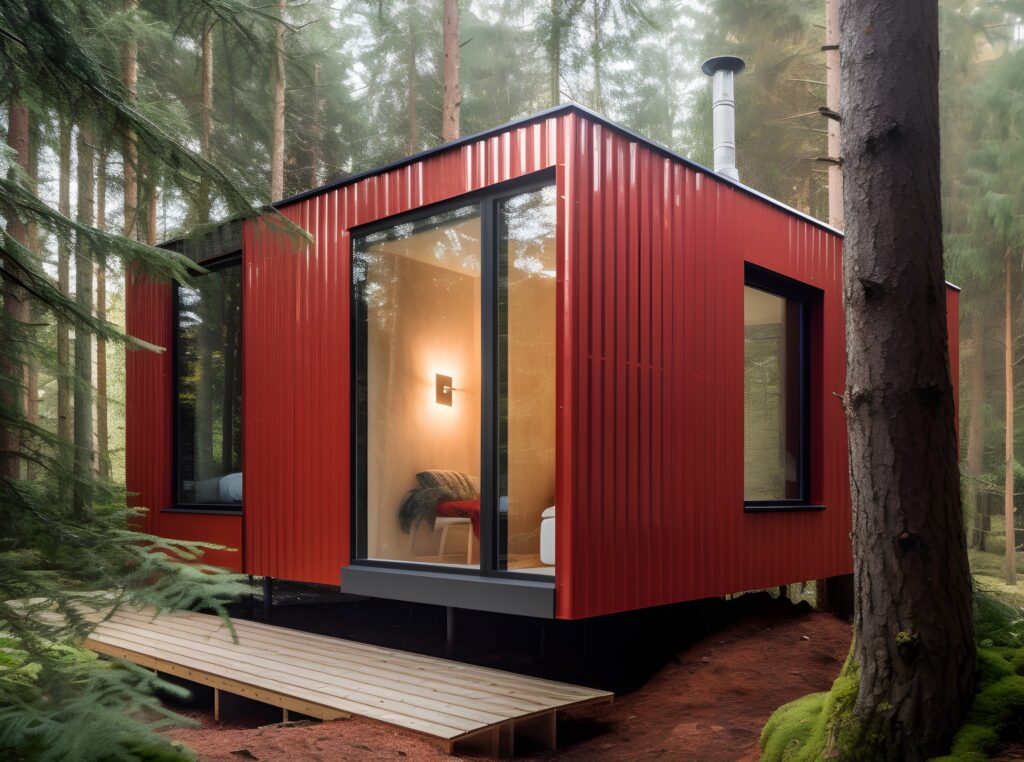

Recycled steel, particularly in container design, emerges as a top contender for eco-friendly building materials owing to its durability, resource conservation, and energy efficiency. By repurposing steel containers, builders not only reduce the demand for virgin materials but also divert waste from landfills, embodying principles of circular economy and sustainability. These containers offer inherent structural integrity and thermal properties, facilitating rapid construction and minimizing energy consumption for heating and cooling.
Additionally, their adaptability allows for versatile design options, promoting creativity and innovation in tiny house construction while fostering sustainable lifestyles through minimalism and off-grid living. Overall, steel container tiny houses represent a holistic approach to eco-friendly living, combining resilience, efficiency, and community engagement in pursuit of a greener future. For more on Container Design see: ‘The Ultimate Guide to Container Homes’
Bamboo: The Eco-Friendly Wonder Material

Bamboo is hailed as one of the most sustainable building materials due to its rapid growth rate, renewability, and versatility. Here’s how bamboo can be effectively utilized as a sustainable building product both for interior and exterior applications.
Exterior Applications:
- Structural Elements: Bamboo’s exceptional tensile strength makes it suitable for structural components such as beams, columns, and trusses.
- Siding and Cladding: Bamboo siding and cladding provide a durable and aesthetically pleasing exterior finish for tiny houses
- Decking and Flooring: Bamboo decking offers a sustainable alternative to traditional wood decking materials. Bamboo boards are highly resistant to moisture, insects, and decay, making them suitable for outdoor use in decking applications.
- Roofing: Bamboo roofing materials, such as bamboo shingles or tiles, provide a natural and sustainable roofing solution for tiny houses.
Interior Applications:
- Flooring: Bamboo flooring is prized for its durability, resilience, and natural beauty. Bamboo planks or tiles can be installed in various patterns, including traditional tongue-and-groove, click-lock, or floating floor systems, to create a stylish and sustainable interior flooring solution for tiny houses.
- Cabinetry and Millwork: Bamboo plywood and solid bamboo boards are commonly used for interior cabinetry, shelving, and millwork in tiny houses.
- Wall Paneling: Bamboo wall paneling adds warmth, texture, and natural beauty to the interior of tiny houses. Bamboo panels can be installed as wainscoting, accent walls, or full-wall coverings to create visual interest and enhance the ambiance of the living space.
- Furniture and Fixtures: Bamboo furniture and fixtures, such as tables, chairs, countertops, and vanities, are popular choices for tiny house interiors.
By incorporating bamboo into both the interior and exterior of tiny house construction, homeowners can enjoy the benefits of a sustainable, durable, and aesthetically pleasing living space while minimizing their environmental footprint. Whether used for structural support, finishes, or furnishings, bamboo offers endless possibilities for creating eco-friendly and stylish tiny homes that harmonize with nature.
Cork: Natural Insulation for Eco-Friendly Comfort

Cork is a renewable and biodegradable material that offers excellent insulation properties, making it ideal for tiny house construction. This type of insulation can help regulate temperature and reduce energy consumption in your tiny home.
Before making a purchase, be sure to research different suppliers, compare prices and product specifications, and verify the availability of cork insulation for your specific project requirements. Additionally, consider factors such as delivery options, return policies, and customer reviews to ensure a positive buying experience.
Overall, cork insulation offers a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to conventional insulation materials, providing effective thermal and acoustic performance while supporting the preservation of cork oak forests and biodiversity in Mediterranean ecosystems. By sourcing cork insulation from reputable suppliers and manufacturers, builders can contribute to energy-efficient and sustainable building practices while creating healthy and comfortable living environments.
Straw Bales: Building with Nature’s Own Insulation
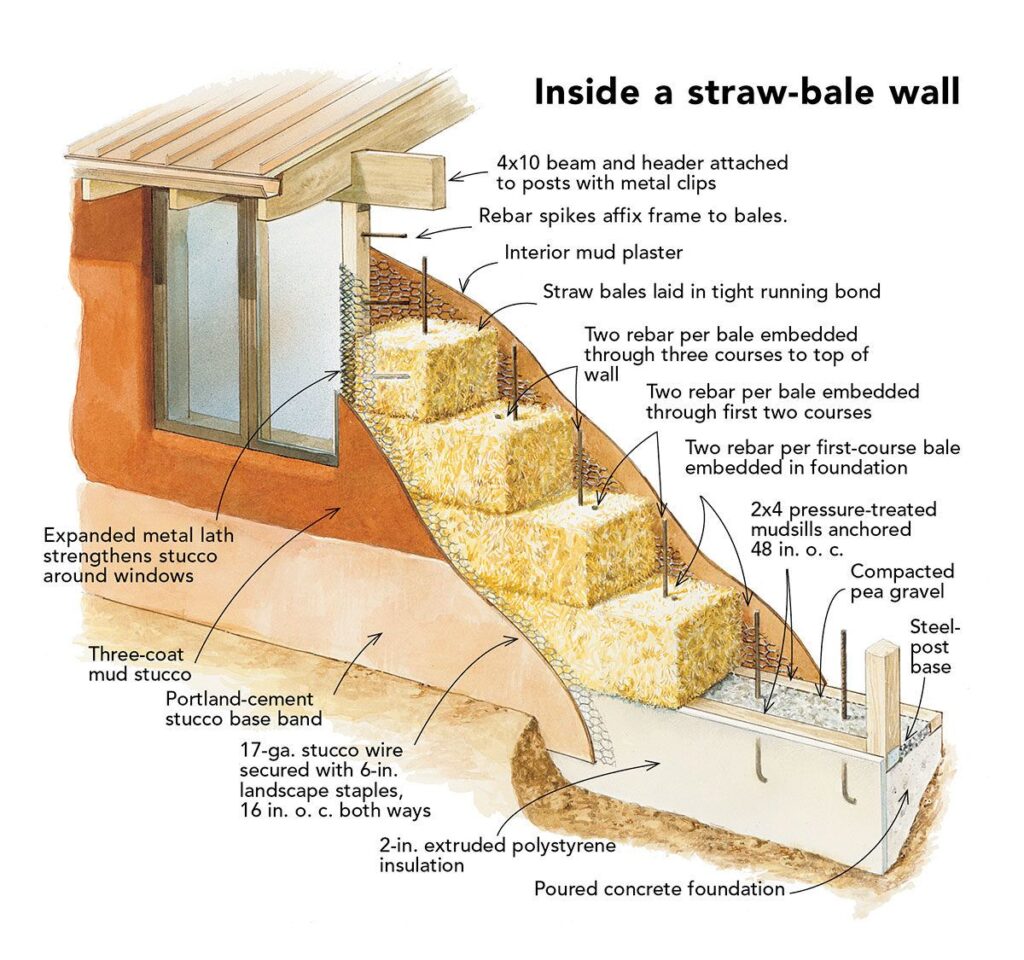
Straw bale construction is an ancient building technique that has experienced a resurgence in popularity due to its sustainability and energy efficiency. You can use straw bales to create super-insulated walls for an eco-friendly tiny house is an innovative and sustainable building technique that offers excellent thermal performance and environmental benefits. Here’s how straw bales can be effectively utilized to achieve super-insulated walls in a tiny house:
1. High R-Value: Straw bales have a high insulation value, typically ranging from R-30 to R-40 per wall. This means that straw bale walls provide superior thermal resistance compared to traditional insulation materials like fiberglass or foam board. By stacking multiple layers of straw bales or combining them with other insulation methods, such as earthen plaster or rigid foam panels, you can further enhance the overall insulation value of the walls.
2. Natural and Renewable: Straw bales are made from agricultural byproducts such as wheat, barley, or rice straw, making them a natural and renewable insulation material. Using straw bales as insulation reduces reliance on non-renewable resources and minimizes environmental impact. Additionally, straw bales are biodegradable and compostable at the end of their useful life, further enhancing their eco-friendliness.
3. Breathability and Moisture Regulation: Straw bale walls have inherent breathability, allowing moisture to pass through without trapping it inside the wall cavity. This breathability helps regulate indoor humidity levels and prevents moisture buildup, reducing the risk of mold and mildew growth. Properly constructed straw bale walls with breathable finishes, such as lime or clay plaster, promote healthy indoor air quality and comfort in the tiny house.
4. Carbon Sequestration: Incorporating straw bales into the construction of a tiny house helps sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Agricultural straw is composed primarily of cellulose, which captures and stores carbon during the growing process. By using straw bales as insulation, you’re effectively locking carbon away in the walls of your tiny house, contributing to carbon neutrality and mitigating climate change.
5. DIY-Friendly Construction: Building with straw bales is relatively simple and accessible, making it suitable for DIY tiny house builders. With basic construction skills and proper guidance, individuals can stack and secure straw bales to create insulated walls without the need for specialized equipment or expertise. Additionally, straw bale construction fosters a sense of community and collaboration, as it often involves teamwork and hands-on participation in the building process.
6. Aesthetic Versatility: Straw bale walls offer aesthetic versatility and design flexibility, allowing for creative expression and customization in tiny house construction. The natural texture and warm tones of straw bales can create a rustic and inviting interior ambiance, complementing various architectural styles and interior décor preferences. With the application of natural finishes such as clay or lime plaster, straw bale walls can be transformed into beautiful and tactile surfaces that enhance the overall visual appeal of the tiny house.
When purchasing straw bales for insulation, consider factors such as bale size, quality, and transportation logistics to ensure they meet your project requirements. Additionally, inquire about any local building codes or regulations regarding the use of straw bales as insulation to ensure compliance with relevant standards.
In summary, using straw bales to create super-insulated walls for an eco-friendly tiny house combines energy efficiency, sustainability, and natural beauty. By harnessing the thermal properties of straw bales and incorporating them into the construction process, tiny house builders can create comfortable, healthy, and environmentally responsible living spaces that embody the principles of sustainable design and off-grid living.
Waste Reduction Strategies

Minimizing waste during the construction process is another essential aspect of eco-friendly tiny house construction. By reusing materials, recycling waste, and adopting sustainable building practices, you can significantly reduce your environmental impact and contribute to a greener future. Here are some waste reduction strategies for the use of eco-friendly building materials in tiny house construction:
1. Material Selection: Choose building materials that are durable, locally sourced, and have minimal packaging to reduce waste generated during construction. Opt for sustainably harvested wood, recycled or salvaged materials, and low-impact alternatives such as bamboo or cork flooring.
2. Reuse and Repurpose: Prioritize the reuse and repurposing of materials wherever possible. Salvage lumber, doors, windows, and fixtures from demolition sites or architectural salvage yards for use in your tiny house construction. Repurpose materials such as pallets, shipping containers, or reclaimed wood for structural elements, siding, or interior finishes.
3. Recycling Program: Implement a comprehensive recycling program on the construction site to collect and segregate recyclable materials such as cardboard, paper, plastic, metal, and glass. Provide clearly labeled recycling bins or containers and educate workers on the importance of recycling and waste diversion.
Construction Waste Management Plan: Develop a waste management plan that outlines procedures for sorting, recycling, and disposing of construction waste responsibly. Assign responsibilities to contractors and subcontractors for waste segregation and disposal according to local regulations and recycling guidelines.
4. On-Site Material Processing: Explore opportunities for on-site material processing to reduce waste and maximize resource efficiency. Use portable sawmills to mill lumber from fallen trees or salvage logs, turning them into dimensional lumber for framing or finishing. Crush concrete or masonry rubble to create aggregate for sub-base or backfilling applications.
5. Lean Construction Practices: Adopt lean construction principles to minimize waste and optimize workflow efficiency. Plan construction activities carefully to avoid overordering materials or excess inventory buildup. Optimize material cuts and use prefabrication techniques to minimize offcuts and waste during assembly.
6. Deconstruction over Demolition: Choose deconstruction over demolition whenever possible to salvage reusable materials and minimize waste generation. Deconstruction involves carefully dismantling structures to recover valuable materials for reuse or recycling, reducing the need for new resource extraction and landfill disposal.
7. Composting Organic Waste: Implement a composting program to manage organic waste generated during construction, such as wood scraps, sawdust, and landscaping debris. Use composting bins or piles to decompose organic matter into nutrient-rich compost for soil amendment or landscaping purposes.
By incorporating these waste reduction strategies into your tiny house construction project, you can minimize environmental impact, conserve resources, and contribute to a more sustainable built environment. Through careful planning, material selection, and construction practices, eco-friendly tiny house builders can create homes that are not only efficient and functional but also environmentally responsible.
Sourcing Green Building Materials:
When purchasing green construction materials for your construction project, you can explore various options, including specialty green building supply stores, online retailers, and larger home improvement chains. Here are some stores where you can potentially buy the green building materials that you are hoping to use in your tiny home build:
1. Specialty Green Building Supply Stores: These stores specialize in eco-friendly and sustainable building materials and offer a wide range of green construction products. Examples include:
2. Online Retailers: Many online retailers provide a diverse selection of green construction materials, making it convenient to shop from anywhere. Some popular online platforms include:
3. Local Hardware Stores and Building Supply Centers: While not all local hardware stores may carry a wide range of green materials, some may offer eco-friendly options or be willing to special order them. It’s worth checking with local suppliers to see what they have available.
4. Specialized Eco-Friendly Suppliers: These suppliers focus exclusively on eco-friendly building materials and may offer a more comprehensive selection than general building supply stores. Green Organizations and Councils are also a great source for locating green materials. Examples include:
5. Manufacturer Websites: Many manufacturers of green construction materials have their own websites where you can learn about their products, specifications, and availability. Some manufacturers may offer direct sales or provide a list of authorized distributors and retailers. Visiting manufacturer websites can help you gather information and locate retailers carrying specific green products.
6. Architectural Salvage Yards: These yards specialize in reclaimed and salvaged building materials, including wood, brick, metal, and fixtures. Architectural salvage yards are treasure troves for finding unique and sustainable materials for construction and renovation projects.
7. Local Sustainable Building Organizations: Some regions have organizations dedicated to promoting sustainable building practices and may maintain lists of local suppliers and resources for green construction materials. These organizations can provide valuable guidance and support in sourcing green materials.
8. Green Home Tours and Expos: Green home tours and expos often feature exhibitors showcasing eco-friendly building materials and technologies. Attending these events can provide opportunities to learn about new products, connect with suppliers, and get inspiration for your project.
By exploring these sources, you can find a wide range of green construction materials to meet your sustainability goals and create environmentally responsible building projects.
Sustainable Construction Techniques
In addition to choosing eco-friendly building materials and implementing energy-efficient design principles, adopting sustainable construction techniques can further enhance the environmental performance of your tiny house. From modular construction to natural building methods, there are many innovative approaches to explore.
Conclusion
Building an eco-friendly tiny house is not only a rewarding endeavor but also a responsible choice for those who care about the environment. By choosing sustainable materials, implementing energy-efficient design principles, and adopting waste reduction strategies, you can create a comfortable and environmentally friendly home that reflects your values and lifestyle.
FAQs
1. Is it more expensive to build an eco-friendly tiny house?
Building costs for eco-friendly tiny houses can vary depending on factors such as material choices, design complexity, and labor costs. While some sustainable materials may have a higher upfront cost, they can result in long-term savings through reduced energy consumption and maintenance expenses.
2. Are there any financing options available for eco-friendly tiny house construction?
Financing options for eco-friendly tiny house construction may include personal loans, green mortgages, and crowdfunding platforms. It’s essential to explore various financing options and choose the one that best fits your financial situation and project goals.
3. How long does it take to build an eco-friendly tiny house?
The construction timeline for an eco-friendly tiny house can vary depending on factors such as the size of the home, the complexity of the design, and the availability of materials and labor. In general, building a tiny house can take anywhere from a few weeks to several months, with eco-friendly construction techniques often requiring additional time for sourcing sustainable materials and implementing energy-efficient systems.
4. What permits and regulations do I need to consider for eco-friendly tiny house construction?
Permit requirements and building codes for tiny houses vary depending on location, so it’s essential to research local regulations before starting construction. Some areas may have specific zoning ordinances or minimum size requirements for dwellings, while others may offer incentives or exemptions for eco-friendly building practices.
5. Can I live off-grid in an eco-friendly tiny house?
Yes, many eco-friendly tiny houses are designed to be off-grid, meaning they are self-sufficient in terms of energy and water supply. Off-grid systems typically include renewable energy sources such as solar panels or wind turbines, as well as water catchment and filtration systems. Living off-grid in a tiny house allows you to minimize your environmental impact while enjoying greater independence and autonomy.
By addressing these frequently asked questions, you can gain a better understanding of the practical considerations and challenges involved in eco-friendly tiny house construction, empowering you to embark on your sustainable building journey with confidence. Whether you’re a seasoned builder or a first-time homeowner, building an eco-friendly tiny house is a rewarding endeavor that offers countless benefits for both you and the planet.





